What is USB flash memory?
Definition and Overview
USB flash memory, often referred to as a USB flash drive, thumb drive, or pen drive, is a small, portable device that uses flash memory to store data. These devices generally connect to a computer via a USB (Universal Serial Bus) port, providing a convenient method for data transfer and storage.
How Does USB Flash Memory Work?
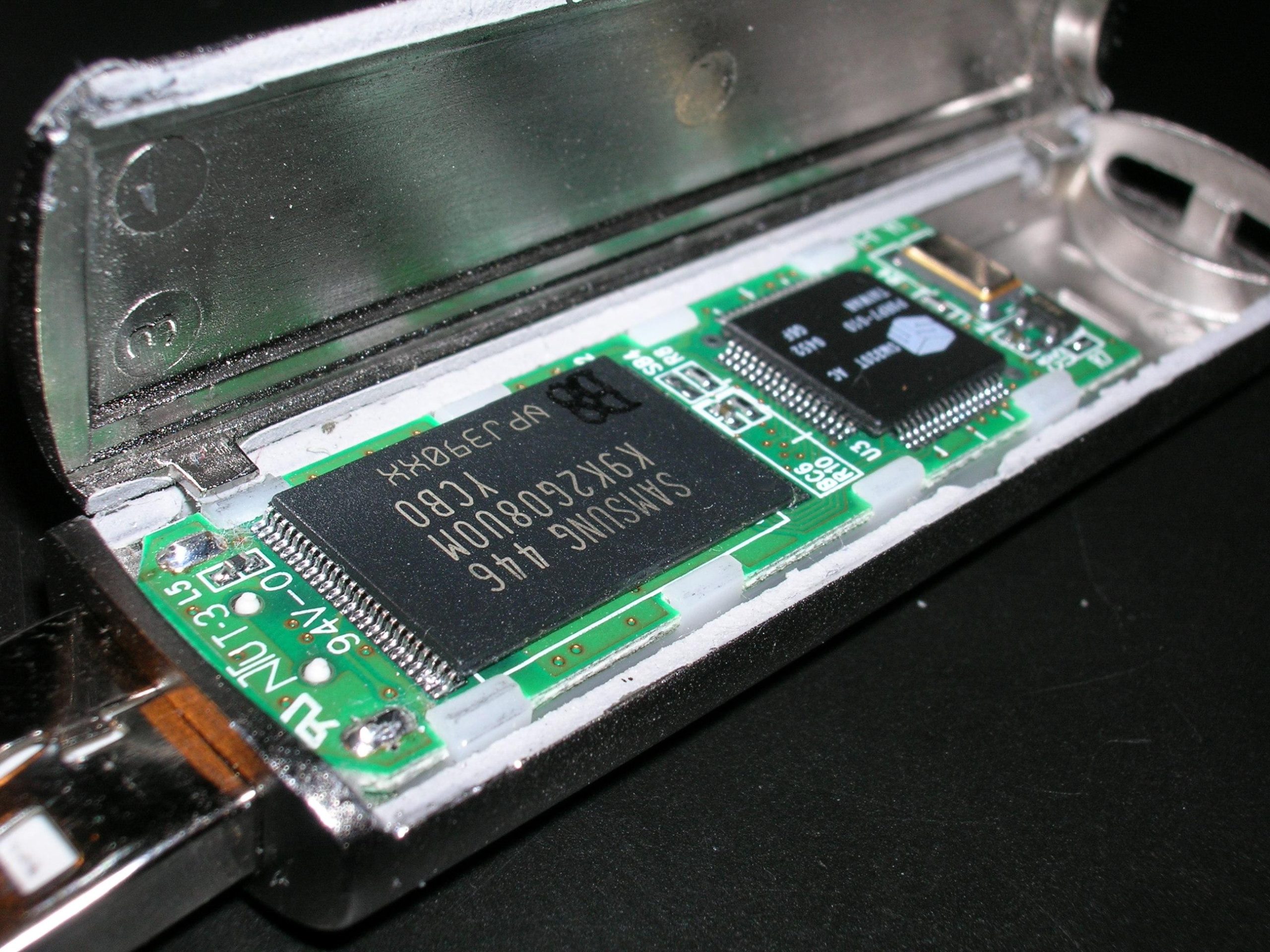
USB flash memory operates using NAND-type flash memory to store data. The device includes a small printed circuit board encased in a durable shell, with electrical contacts that interface with a USB port. When connected to a computer, the flash drive can read and write data, functioning as a secondary storage device.
Components of USB Flash Memory
- USB Connector: The interface through which the flash drive connects to the computer.
- USB Mass Storage Controller: Manages the data transfer between the computer and the flash memory chip.
- NAND Flash Memory Chip: Stores the actual data.
- Crystal Oscillator: Generates the clock signal to synchronize data transfer.
Benefits of USB Flash Memory
USB flash memory offers numerous advantages that make it a popular choice for data storage and transfer:
- Portability: Its compact size allows you to carry large amounts of data easily.
- Durability: Solid-state design means there are no moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
- Compatibility: Works across different operating systems and devices.
- Capacity: Available in a wide range of storage sizes, from 1GB to several terabytes.
- Speed: High-speed data transfer capabilities with USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 versions.
USB Flash Memory Types
There are different types of USB flash drives based on their interface and purpose:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard USB Drive | Basic design with USB 2.0 or USB 3.0 interfaces, suitable for general data storage. |
| Secure USB Drive | Includes encryption features for protecting sensitive data. |
| Ultra-compact USB Drive | Smaller in size, designed for enhanced portability. |
| OTG USB Drive | Features a dual connection (USB and micro-USB or USB-C) for use with mobile devices. |
Practical Tips for Using USB Flash Memory
Maximize the lifespan and performance of your USB flash drives with these helpful tips:
- Safely Eject: Always use the “Eject” option on your computer before unplugging the drive to prevent data corruption.
- Keep It Clean: Protect the USB connector from dust and debris that could interfere with data transfer.
- Backup Regularly: Flash drives can fail; regularly backup important data to avoid data loss.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Store your USB flash drives in a cool, dry place to prevent damage to the NAND flash memory chip.
- Use Virus Scans: Regularly scan your USB drives to keep them free from malware and viruses.
Common Uses of USB Flash Memory
USB flash drives are incredibly versatile and can be used for a variety of purposes:
- Data Transfer: Easily transport files between different computers or devices.
- Backup Storage: Create backups of important documents, photos, and videos.
- Media Players: Store music and videos for playback on compatible media players.
- Portable Applications: Run applications directly from the flash drive without installing them on a computer.
- Bootable Drives: Install operating systems or software, particularly useful for troubleshooting or setting up new systems.
Interesting Facts About USB Flash Memory
- The first USB flash drive was introduced by IBM in 2000 with a storage capacity of 8MB.
- USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, marking its universal compatibility with different devices.
- USB 3.0 offers transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbps, which is significantly faster than USB 2.0’s 480 Mbps.
- The largest USB flash drive currently available boasts a capacity of up to 2TB.
“`